NTIA Broadband Map, Senators’ Cybersecurity Bill, U.S. and EU Reveal Transatlantic Council
The NTIA unveils new broadband map, a new cybersecurity bill against equipment buys, U.S. and EU partner on tech council.
Jasmine Campos
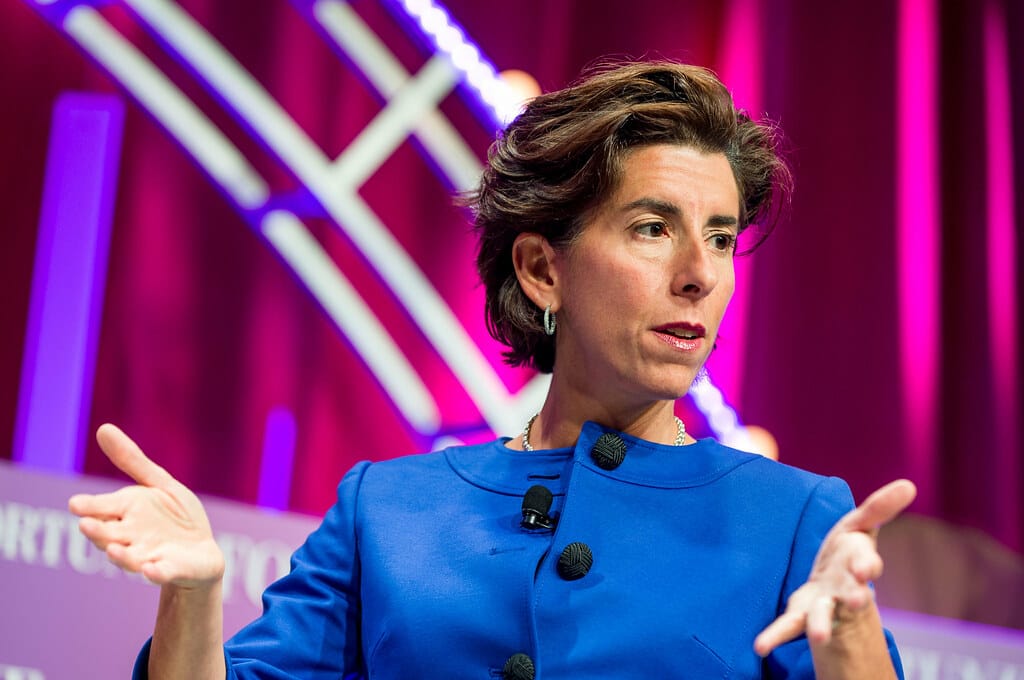

June 17, 2021 – The National Telecommunications and Information Administration released an interactive map that shows areas of the country with and without the Federal Communications Commission’s baseline speeds of 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload speeds.
It’s the first interactive map of its kind that will allow users to explore datasets from both public and private sources.
“As we release this important data to the public, it paints a sobering view of the challenges facing far too many Americans as they try to connect to high-speed broadband and participate in our modern economy,” said U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo.
The map also allows users to see the connection between broadband access and general income level.
Evelyn Remaley from the NTIA said of the map that, “Any effort to close the digital divide starts with solid data, and NTIA continues to help policymakers make more informed decisions on expanding broadband access.”
FCC Acting Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel said the map is a “welcome new tool” toward ensuring that every household has the internet access they need.
Eshoo, Scalise Introduce Cybersecurity Protections Bill
Reps Anna Eshoo, D-California, and House Republican Whip Steve Scalise, R-Louisiana, introduced Tuesday the Secure Equipment Act of 2021 to combat cyber security issues.
The legislation would prohibit the Federal Communications Commission from providing new equipment licenses to any companies that pose a national security threat.
Though the FCC has made delineations about which companies have posed national security threats, they have only prevented federal funds from being used to purchase those items. The goal of this legislation would be to take those items out of the American market.
In April, FCC Commissioner Brendan Carr said loopholes allowing the private purchase of Chinese goods, considered by the U.S. government as a threat, must be closed. In a statement Tuesday, Carr said the bill would “close a glaring loophole that Huawei and other entities are exploiting today to place their insecure gear into our networks.”
Eschoo added that, “Our legislation would further strengthen U.S. telecommunications networks by prohibiting equipment manufactured by entities that are a threat to our national security.”
Scalise added that, “China must be stopped from doing further damage to our telecommunications network, and I’m proud to sponsor this important legislation with Rep. Eshoo to strengthen our national security and stand up to subsidiaries of the Chinese Communist Party.”
The act is the latest in a series attempting to combat increased cyber warfare on American products.
U.S., EU to Create Trade and Technology Council
The U.S. and European Union announced Tuesday the creation of the Trade and Technology Council, a tool being used to combat China’s rising economy.
The Council, which will be established by the transatlantic partners, will create new rules surrounding trade that would facilitate research and development in the respective economies. It is to be made up of top officials from both nations, including U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken.
According to CNBC, the goals of the council are three-fold: to create new global trade standards as technology advances, use the internet to promote democratic values, and to collaborate on cutting-edge research and development.
In a joint statement, USTelecom and the European Telecommunications Network Operators’ Association (ETNO) said they “welcome the strengthening of the transatlantic dialogue on industrial and policy approaches to technology.”
The associations emphasized that they are “resolute” in creating policy that yields a “confident and equitable vision for the digital future of all our citizens.”
The two nations have also set up a Joint Technology Competition Policy dialogue, showing the importance they feel should be placed on “developing common approaches and strengthening the cooperation on competition policy and enforcement in the tech sectors.”









Member discussion