Experts Suggest Measures to Protect Affordable Connectivity Program at Senate Hearing
Under consideration: Opening the Universal Service Fund to contributions from broadband and Big Tech companies.
Hanna Agro
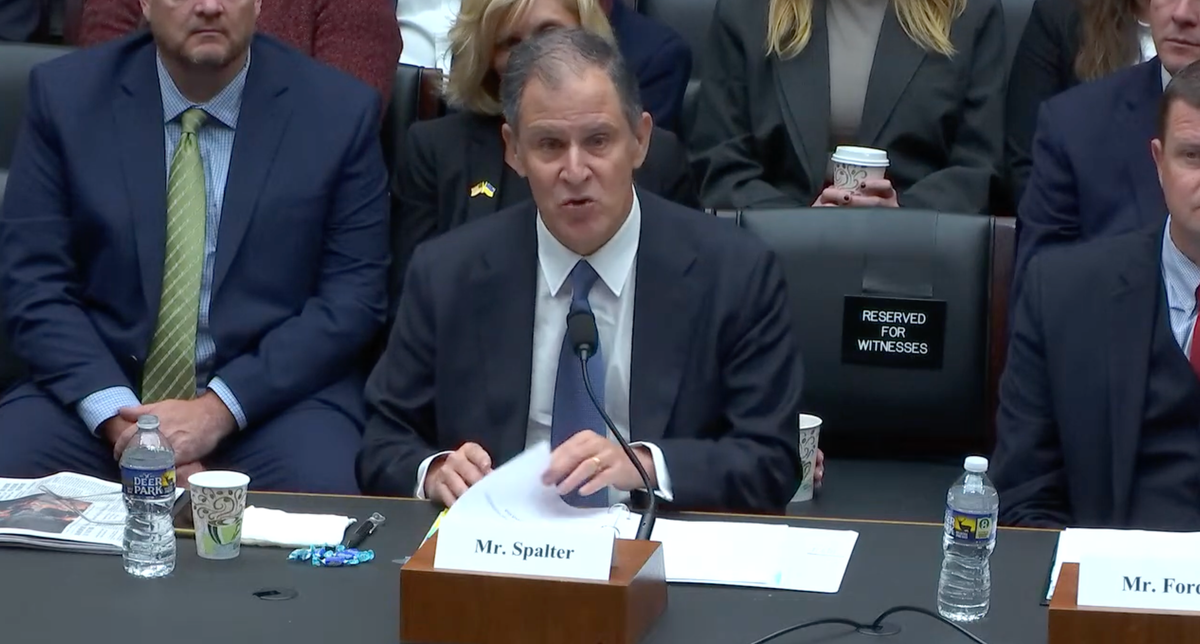
WASHINGTON, September 28, 2023 – A broadband association asked Congress last week to open the Universal Service Fund to contributions from broadband and Big Tech revenues to allow the umbrella fund to absorb and support the Affordable Connectivity Program.
The industry is concerned that the $14-billion ACP program, which discounts monthly services for low-income Americans and those on tribal lands, is going to run out of money by early next year. Meanwhile, it is universally agreed that the Universal Service Fund, which includes four high-cost broadband programs, is struggling to maintain its roughly $8-billion annual pace without a diversification of its revenue sources.
Jonathan Spalter, president and CEO of USTelecom, told the Communications and Technology subcommittee studying the future of rural broadband on September 21 that Congress could both support the sustainability of the USF and the ACP by forcing contributions from broadband and Big Tech revenues.
The idea is that the extra revenue would solve the USF sustainability question by allowing the fund to continue to support the existing four programs under its purview, while also allowing it to adopt the ACP program, hence removing that program from reliance on Congress for money.
“We can have Congress give the FCC the authorities that it requires to be able to expand the contribution base, integrating the ACP within USF program, and thereby allowing the potentially out of control contribution factor that will potentially bog down the viability and longevity of the Universal Service Fund mechanisms to go down,” Spalter said.
“And in so doing it can expand the contribution base sufficiently to allow not only broadband but importantly the dominant Big Tech companies to participate so that we would effectively fuse the Affordable Connectivity Program with [high-cost program] Lifeline and do so in a way that would actually not require appropriated dollars from Congress.”
The ACP currently has around 21 million Americans signed up, but the FCC says many more are eligible. The commission has been allocating money to outreach groups to market the subsidy program.
While some have argued that the Federal Communications Commission could unilaterally expand the contribution base of the USF, the commission has elected to wait for Congress to make the requisite legislative reforms to give it that authority.
Forcing Big Tech companies, which rely on the internet to deliver their products, has been an idea tossed around by experts and promoted by Federal Communications Commissioner Brendan Carr. Meanwhile, forcing broadband revenues to contribute to the fund has also received good support.
The concern for the ACP program is that the internet service providers rely on the $14 billion to continue to offer discounts.
“With funding set to be depleted early next year, initial notices of service termination could be out during the height of the holiday season in December – that’s a present none of our constituents deserve to receive,” said Congresswoman Doris Matsui, D-Calif.
“Poverty is everywhere, but higher in rural America, in our region the reason most people can’t adopt service is due to lack of affordability, this impacts more households than lack of infrastructure alone,” said Sara Nichols, senior planner of the Land of Sky Regional Council of Government.
“It’s a program we simply can’t afford to lose,” added Nichols.










Member discussion