Lawmakers Debate Clean Energy’s Role in Resolving Supply Chain Fragility, China Concerns
The U.S. accounts for just 10 percent of electric vehicle production and 7 percent of battery production.
Em McPhie
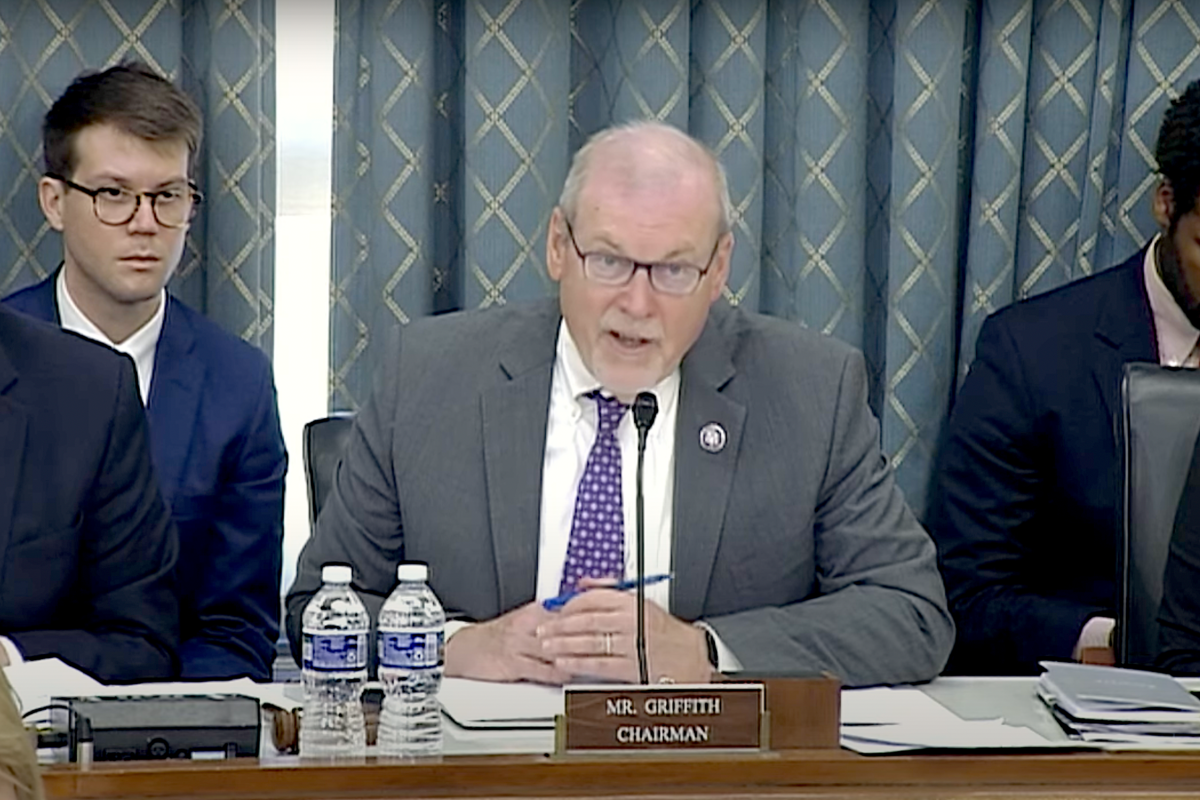

WASHINGTON, May 23, 2023 — As historic federal investments in infrastructure, manufacturing and clean energy begin to take effect, House lawmakers on Tuesday clashed over the best response to shared concerns about competition with China and the instability of domestic electricity sector supply chains.
Tuesday’s hearing, convened by the House Oversight and Investigations Subcommittee, came just one day after the Department of Energy announced that it would no longer be awarding a $200 million grant to Texas-based battery company Microvast, following intense scrutiny from Republican lawmakers over the company’s ties to China.
Subcommittee Chair Morgan Griffith, R-Va., praised the decision but expressed continued skepticism about the department’s vetting processes — emphasizing the absence of Office of Manufacturing Director David Howell, who declined an invitation to testify.
By failing to appear at the hearing, “the Department of Energy not only refused to provide transparency to this committee, but they’re refusing to be transparent to the American people, who deserve every assurance that their tax dollars are not being funneled to China,” said Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers, R-Wash., chair of the full Energy and Commerce Committee.
But Committee Ranking Member Frank Pallone, D-N.J., argued that the award reversal was proof that the department “is taking its stewardship of taxpayer money very seriously.”
Pallone also blamed the Republican majority for Howell’s absence, claiming that the hearing had originally been planned for June and that department officials were working to coordinate the schedule “when all of sudden the date changed earlier this month to today.”
The proposed Microvast award would have been part of a $2.8 billion investment in battery manufacturing funded by the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021, intended to accelerate and strengthen a domestic supply chain. The United States currently accounts for just 10 percent of global electric vehicle production and 7 percent of battery production capacity.
By contrast, China produces three-quarters of all lithium-ion batteries and is home to the majority of production and processing capacity for several key battery components. China was responsible for half of the growth of the electric vehicle market in 2021, according to a recent International Energy Agency report.
While the Biden administration has taken steps to bolster U.S. manufacturing through the IIJA and the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, Republicans have broadly criticized this approach — particularly the IRA’s focus on clean energy.
Because of the current manufacturing imbalance, the administration’s emphasis on electric vehicles will largely benefit China rather than the U.S., argued Diana Furchtgott-Roth, director of the Heritage Foundation’s Center for Energy, Climate and Environment.
“Heavily subsidizing renewable energy and shoveling money in the form of financial awards out the door is not the solution,” McMorris Rodgers said. “These policies undermine our energy security and financially burden Americans already struggling with high cost of living — and would leave us even more reliant on China.”
However, a study commissioned by Third Way and Breakthrough Energy indicated that these pieces of legislation, alongside the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, are “fostering investments in and a reshoring of the clean energy supply chain and the associated manufacturing base,” said Ellen Hughes-Cromwick, senior resident fellow for the climate and energy program at Third Way.
Hughes-Cromwick urged lawmakers to allow time for supply chain restructuring, saying that policy stability over multiple years is crucial to allow companies to make sustainable adjustments.
In order to achieve domestic clean energy goals, Congress should first modernize permitting, said Jeremy Harrell, chief strategy officer at ClearPath.
“The single largest mover of private sector investment is regulatory certainty,” Harrell claimed. “Never has the phrase ‘time is money’ been more appropriate — developers can only build new energy infrastructure as fast as federal, state and local governments can permit them, and right now that’s not fast enough.”








Member discussion