Starlink Allowed to Operate in Portions of National Radio Quiet Zone
Residents in the quiet zone in Virginia and West Virginia now have the option for satellite internet.
Ari Bertenthal
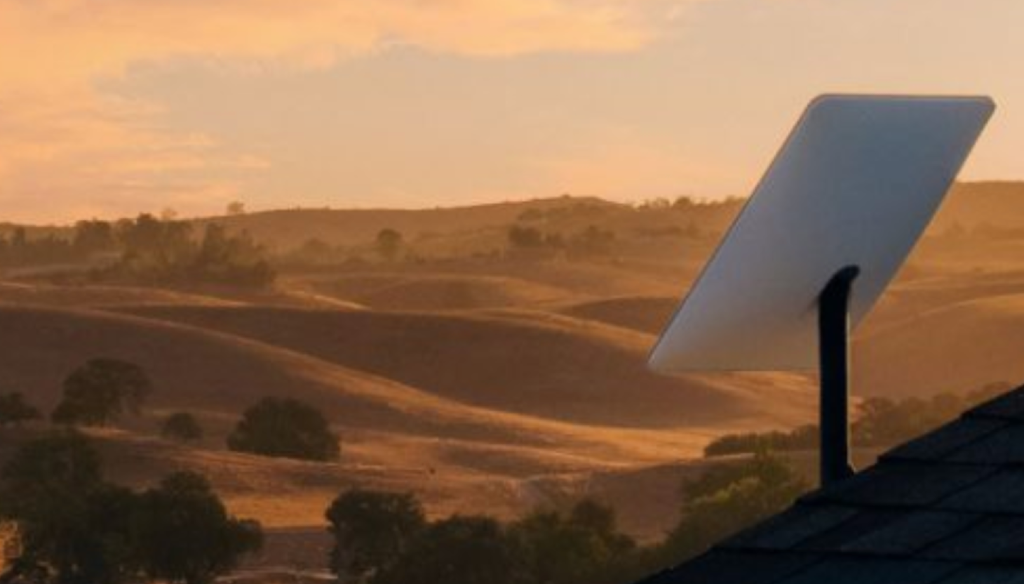

WASHINGTON, Oct. 31, 2024 - A large portion of Virginia and West Virginia residents within the National Radio Quiet Zone are now eligible to receive high speed satellite internet service after a nearly three year effort.
The newly established option for residents of the NRQZ to receive satellite internet is a result of a collaborative effort between the National Science Foundation, Elon Musk’s Starlink and the National Radio Astronomy Observatory.
The announcement was made on the NSF website on Oct. 25.
The NRQZ, established in 1958, is an area where federal restrictions on radio transmissions apply in order to protect scientific research and national security operations which rely on a quiet radio environment to detect faint signals.
The NRQZ is about 13,000 square miles and includes about 8,000 people.
SpaceX began a one year assessment period Saturday to provide 99.5 percent of NRQZ residents with residential satellite internet service after coordinating with the NSF and National Security Agency since 2019 to maximize internet service without hindering the objectives of the NRQZ.
“This collaboration will allow residents to access high quality, high speed internet, and also expand opportunities for improved communication, like those needed by emergency services and first responders,” Jim Jackson, the NSF Green Bank Observatory Director said.
During the one year assessment period, scientists and engineers planned to tackle any interference issues without interrupting internet service.










Member discussion