Data, Competition and Affordability Key to Expanding Broadband
Key recent developments include FCC fines on nine ISP, the annual 706 Report and a pending deadline for the FCC's broadband labels program.
Jericho Casper

WASHINGTON, September 21, 2024 – Expanding broadband access to all Americans will require accurate data collection and mapping to ensure that funding and resources are allocated effectively.
This was the central theme of the Broadband Breakfast Live Online event on Wednesday, where industry leaders discussed current challenges and opportunities in the development of broadband mapping and data.
 Broadband BreakfastBryan Darr
Broadband BreakfastBryan Darr
Recent developments, they said, have underscored the growing importance of transparency in broadband data and mapping:
- The Federal Communications Commission issued fines to nine Internet providers for withholding data from the Broadband Data Collection;
- The FCC launched the 18th annual Section 706 Report inquiry, examining the progress in the deployment of advanced telecommunications capabilities nationwide;
- Starting October 10, all ISPs will be required to comply with the FCC’s broadband label rules, which mandate clear disclosures to consumers at the point of sale;and
- The introduction of the bipartisan PROTOCOL Act seeks to enhance coordination between federal agencies’ broadband deployment maps and databases when awarding infrastructure funding.
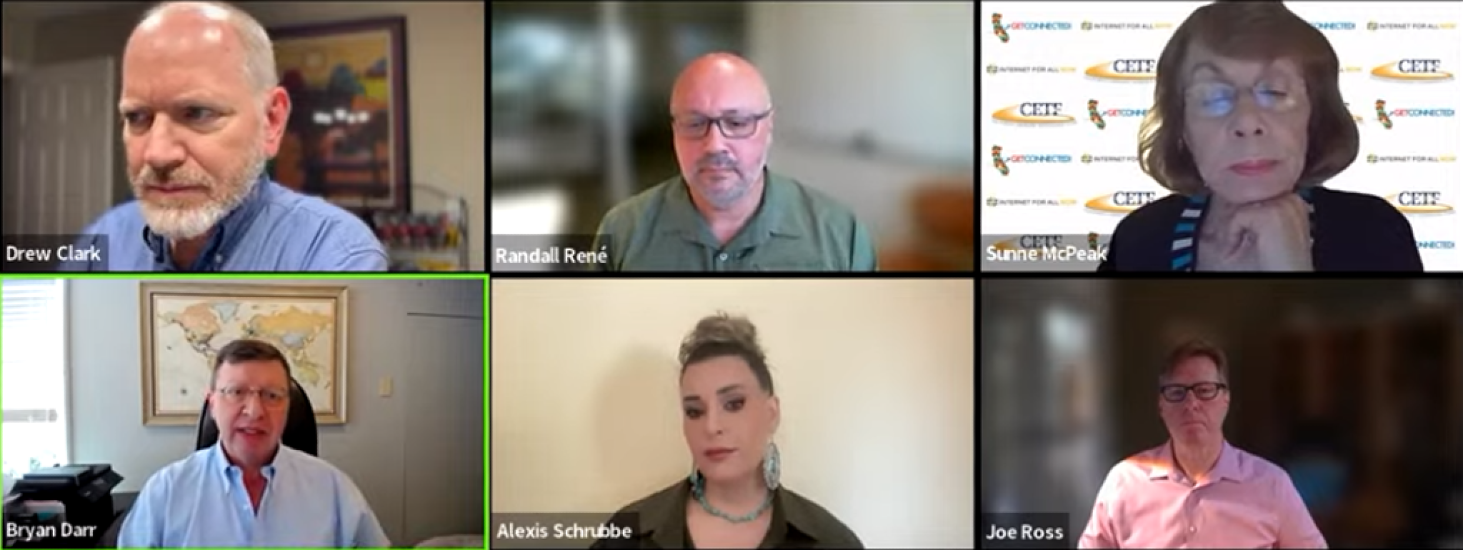
During the event moderated by Drew Clark, CEO of Broadband Breakfast, the panel of experts emphasized the need for transparency, competition, and adoption strategies to support ongoing deployment efforts.
Bryan Darr, vice president of government affairs at Ookla, opened the discussion by focusing on the 5G Fund and the FCC’s ongoing effort to cover underserved rural areas. Darr pointed out the controversy surrounding the FCC’s testing requirements, particularly the exclusion of mobile testing, which is raising costs for operators.
In a filing at the FCC in May, Ookla highlighted issues with data submission, emphasizing that only the FCC's own speed test mobile application is currently functioning as intended, and that certain requirements are hindering the submission of speed test data from apps like Ookla's Speedtest.
Darr stressed the limitations of the FCC’s speed test app, and said that users were required to disclose personal information in order to submit – an approach that Ookla avoids in its enterprise-level drive testing.
Ookla representatives emphasized the importance of expanding the use of crowdsourced data, viewing it as a critical part of analyzing both mobile and fixed broadband availability nationwide.
Sunne Wright McPeak, CEO of the California Emerging Technology Fund, a non-profit organization established by the California Public Utilities Commission to close the digital divide in the state, emphasized the need for adoption strategies to accompany broadband deployment, particularly in the hardest-to-reach areas like tribal lands and high-poverty neighborhoods.
McPeak drew attention to California’s 2023 statewide survey, which revealed that 35.6% of unconnected households cited affordability as the primary barrier to getting online, with only 2.7% citing lack of infrastructure.
She also called for reforms to programs like Lifeline and the Universal Service Fund, and criticized the lack of a permanent replacement for the expired federal Affordable Connectivity Program, which helped connect 2.9 million households in California. McPeak stressed that deployment without adoption efforts leaves many without access to affordable broadband.
Randall René, director of telecom industry solutions at Esri, a global Geographic Information System software company, emphasized that collaboration between government entities and service providers needed to be built on transparency and better data.
René discussed how GIS tools can be leveraged to consolidate disparate legacy systems, providing a comprehensive view of factors such as permitting requirements, sustainability, and resiliency of networks in specific areas. He highlighted the importance of considering environmental risks like floods, fires, and hurricanes before building networks, ensuring that capital is stretched as efficiently as possible.
Joe Ross, senior partner and co-founder of Televate, LLC, a telecommunications consulting firm specializing in broadband infrastructure, public safety communications, and wireless technology, highlighted the role of competition in improving broadband access and reducing costs for consumers.
Ross shared findings from Televate’s broadband competition reports, saying they revealed that while competition has improved, only 60% of locations nationwide have competition at the 100 * 20 Megabits per second (Mbps) level, with rural areas lagging behind.
He noted that in areas with sufficient population density, like Marion County, Fla., competition remains limited despite the affordability of deploying fiber. Ross urged ISPs to address these competition gaps by leveraging data to identify areas where they could expand service cost-effectively.
Dr. Alexis Schrubbe, director of the Internet Equity Initiative at the University of Chicago’s Data Science Institute, echoed McPeak’s emphasis on affordability and the need for real-world measurement of broadband access.
Schrubbe described how the University of Chicago has placed measurement hardware boxes within particular neighborhoods. These devices continuously collect data on network performance over time, providing more reliable and consistent measurements than traditional browser-based speed tests, which can be affected by temporary factors like device performance or network congestion at the time of testing. This method allows for a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of how the network performs in the long term.
Schrubbe recounted a recent distribution event in partnership with the Milwaukee United Way, where residents accepted measurement boxes but indicated they would soon cancel their internet service due to the expiration of ACP subsidies, highlighting the affordability crisis. This real-world interaction demonstrated how measuring broadband access needs to account for the full context of people's lives, not just technical metrics, he said.
Schrubbe concluded by advocating for a more transparent, scientifically rigorous approach to broadband measurement, noting that broadband performance metrics need to be accurate and trustworthy to guide policy and consumer decisions.

September 18, 2024 - Measuring Broadband: What’s the Next Step?
In the evolving world of broadband, measuring connection is as crucial as it is complex. In light of major federal broadband fundings, how do we quantify broadband deployment? Join Broadband Breakfast as we examine lessons from past efforts, debate current metrics, and chart a course for more effective broadband measurement to ensure our investments truly bridge the digital divide.
Panelists:
- Bryan Darr, Vice President, Government Affairs, Ookla
- Joe Ross, Senior Partner and Co-founder, Televate, LLC
- Randall René, Director, Telecom Industry Solutions, Esri
- Sunne Wright McPeak, President and CEO, California Emerging Technology Fund (CETF)
- Alexis D. Schrubbe, Director of the Internet Equity Initiative, University of Chicago’s Data Science Institute
- Drew Clark (moderator), CEO and Publisher, Broadband Breakfast
 Broadband BreakfastBryan Darr
Broadband BreakfastBryan Darr









Member discussion